Furnace Services in Austin
Comprehensive Furnace Repair and Installation in Austin Travis County
Austin's chilly winters demand a reliable furnace to keep your home warm and comfortable. Regular furnace maintenance and timely repairs are essential to ensure your system operates efficiently and prevents unexpected breakdowns.
At Precision Heating & Air, we have been providing top-quality furnace services in Austin since 2008. Our NATE-certified technicians are committed to delivering exceptional service, ensuring your home stays cozy. Trust us for reliable repairs, installations, and maintenance with a 100% satisfaction guarantee.
How Does a Furnace Work
- The furnace burner is located in the air handler box along with a fan.
- The fan blows the heated air into supply ducts, for distribution to registers located throughout the house.
- Air from individual rooms or common areas is drawn into return registers and brought back through return ducts to the furnace air handler where it is reheated and redistributed.
Furnace Efficiency
The efficiency of a furnace or boiler is measured by annual fuel utilization efficiency (AFUE).
What Is an AFUE Rating and What Does It Cover?
- An AFUE of 90% means that 90% of the energy in the fuel becomes heat for the home, and the other 10% escapes out the vent pipe and through the furnace jacket.
- AFUE doesn’t include the power consumption of the fan and controls.
- Nor does it include heat losses of the duct system, which can be up to 30% or more when ducts are leaky, poorly insulated, and located in an uninsulated attic or crawlspace.
If not properly maintained, the actual efficiency of the furnace can be significantly lower than the rated efficiency. Routine maintenance is crucial to maintaining a high AFUE. This includes checking and replacing filters, ensuring burners are clean and intact, and verifying that all components are functioning efficiently.
Low-Efficiency Furnaces (Less than 78%)
While nearly all furnaces sold today have an AFUE of at least 80%, many older, less efficient furnaces in the 56% to 72% range are still in operation, including even old coal burners that have been switched over to oil or gas. Homeowners with these systems may face higher energy bills and reduced comfort levels. Retrofitting or replacing these systems can greatly enhance efficiency. Options include sealing ductwork, integrating energy-efficient controls, or considering an upgrade to a modern high-efficiency furnace, which provides better heating with lower fuel consumption.
How to Check If a Furnace Is Old
- If a furnace has a pilot light, it was probably installed prior to 1992 and likely has an efficiency of less than 72%.
- Old gas furnaces may lack a vent damper (which saves energy by limiting the flow of heated air up the chimney when the heating system is off).
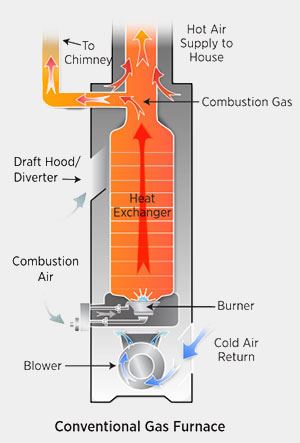
How Does a Natural Draft Furnace Work
Older-style furnaces can be called draft-hood furnaces because they draw combustion and dilution air from the room in which they are located; the dilution air enters through a draft hood (also called a draft diverter). Understanding how natural draft furnaces operate helps in diagnosing common issues like poor air circulation or back drafting, which can affect indoor air quality. Regular inspections ensure that chimneys aren't blocked and that there's adequate ventilation to prevent safety hazards.
How Does an Oil Furnace Work
Oil furnaces use a barometric damper instead of a draft diverter for dilution of air in the chimney or vent system to decouple the burner from the chimney, thus avoiding poor combustion. This feature is designed to optimize efficiency while reducing fuel waste. Routine maintenance of oil furnaces includes checking and adjusting the damper setting, cleaning the burner, and ensuring that all connections are secure to prevent leaks and improve stability.
Call us today at (512) 379-6385 or contact us online for expert furnace solutions in Austin.
What Is Depressurization in a House?
Depressurization is a situation that can occur if more air is being pulled out of the home than is being drawn into the home through air leaks or intentional ventilation. Certain changes in the home can lead to depressurization. It's critical to manage exhaust systems correctly and ensure proper ventilation during renovations or modifications to prevent negative pressure issues. Implementing balanced ventilation systems can help maintain appropriate airflow and prevent exhaust backdrafts.
For example, if a new kitchen range is installed with a high-powered exhaust fan or if a significant amount of air sealing is done. These changes could possibly increase the risk of back drafting, where exhaust products spill back into the house rather than going up the flue.
A certified energy contractor will conduct combustion safety testing as part of any combustion appliance repair or replacement or air sealing project. The testing will ensure that the furnace and combustion appliances have adequate combustion air and are venting properly.
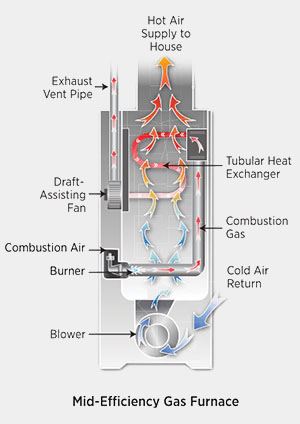
Mid-Efficiency Furnaces (80% to 82%)
Mid-efficiency (80% to 82%) furnaces have no draft hood. Instead, they use fan-assisted draft with a fan located at the outlet (draft inducer) of the heat exchanger to create a regulated flow of combustion air. This design change increased efficiency from 65% AFUE in atmospheric draft furnaces to over 80% in fan-assisted furnaces. Fan-assisted draft minimizes the risk of backdrafting. These systems offer a good balance of performance and cost, and many homeowners find updating to mid-efficiency systems an ideal step forward. They provide sufficient heat while being significantly more energy-efficient than older models.
How to Find Efficiency of Furnace
For furnaces with an oil burner, one way to determine the age and efficiency is to look at the nameplate.
- If the oil furnace has a nameplate motor speed of 1,725 rpm, it is most likely an older model with a less efficient burner.
- Models with a nameplate motor speed of 3,450 are newer than 20 years old and have a flame retention burner that wastes less heat; they have a steady-state efficiency of 80% or more.
Bigger Isn’t Always Better
Many older furnaces and central air conditioning systems are oversized. An energy performance contractor can run energy analysis software to help determine your heating and cooling needs after air sealing and insulation improvements are made. An appropriately sized system operates more efficiently, providing better comfort levels and lower utility bills while reducing wear and tear over time. Modern systems are designed to heat evenly, avoiding the cycling on and off that can occur with oversized units.
How to Calculate Furnace Size
In the past, many HVAC contractors used “rules of thumb” to determine HVAC sizing, and as a result, many installed oversized systems. Today’s trained HVAC contractor should determine your heating and cooling loads, and the right size for your HVAC equipment, based on calculations developed by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA 2005; 1995; 2009).
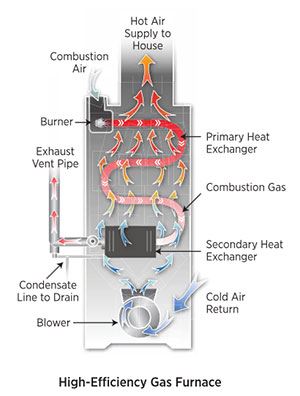
High-Efficiency Furnaces (90% to 98%)
The most efficient furnaces available today are sealed-combustion (direct-vent) condensing furnaces, which have efficiencies of 90% to 98%. By utilizing advanced technology that recaptures latent heat from exhaust, these systems push efficiency boundaries, offering significant cost savings over the furnace’s lifetime. They are ideal in climates with fluctuating temperatures and are designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly.
What Is a High Efficiency Condensing Furnace?
About 12% of the heat from the combustion process is captured in water vapor as latent heat. A condensing furnace condenses this water vapor through a secondary heat exchanger to capture the heat rather than letting it escape up the flue. This results in a warmer and more efficiently heated home. The financial and environmental benefits of condensing furnaces make them a top choice for those interested in sustainable living.
This technological advance enabled gas furnaces to jump from 82% AFUE to 90% AFUE or higher (ACEEE 2011). There are no gas furnaces with AFUE ratings between 83% and 89% because of problems arising from condensation in the heat exchangers that occur within this range.
How Do Condensing Gas Furnaces Work?
High-efficiency condensing furnaces avoid back-drafting issues by having sealed combustion. These furnaces are designed to vent exhaust gases (combustion products) directly to the outside through a dedicated vent pipe. They should also be installed with a second vent pipe to bring outside air directly into the combustion chamber. This dual pipe setup ensures efficient operation and maintains indoor air quality by filtering, heating, and recirculating air in a streamlined process.
Condensing Furnace vs. Non-Condensing Furnace
Although a condensing unit costs more than a non-condensing unit, the condensing unit will save money in fuel costs over its 15- to 20-year life and is a particularly wise investment in cold climates. The up-front investment is often offset by lower monthly heating bills and the eventual increase in property value associated with having an eco-friendly heating solution.
AFUE Ratings of Combustion Furnaces
Nearly all combustion furnaces sold today meet or exceed 80% AFUE. About one-third of current sales on a national basis are 90% AFUE or better. In just the past 10 years alone, about 7.5 million condensing furnaces went into replacement installations in the United States (ACEEE 2011). The growing popularity of these systems indicates a shift toward energy-aware practices among homeowners and aligns with ongoing technological evolution aimed at reducing carbon footprints.
AFUE Ratings of Electric Resistance Furnaces
The AFUE rating for an all-electric resistance furnace or boiler is between 95% and 100%; because there is no combustion, no heat loss occurs up the flue, but there may be some heat loss through the furnace housing. However in some parts of the country, electricity is expensive to purchase and it can be expensive to produce from an environmental standpoint as well, making electric heat a less cost-effective option. Balancing energy costs with environmental impact is essential for choosing the right heating solution.
Why Choose Us for Furnace Solutions in Austin
When it comes to furnace solutions in Austin, our team at Precision Heating & Air stands out for several reasons. We are dedicated to providing top-notch service and ensuring your home stays warm and comfortable throughout the winter months.
- Experienced Technicians: Our NATE-certified technicians have been serving the Austin area since 2008, bringing years of expertise to every job.
- Comprehensive Services: We offer a full range of furnace services, including repairs, installations, and maintenance, tailored to meet your specific needs.
- Quality Assurance: We use 100% American-made parts and provide a 10-year warranty on parts, ensuring long-lasting solutions.
- Customer Satisfaction: Our 100% satisfaction guarantee means we are committed to delivering exceptional service every time.
- Award-Winning Service: We have received multiple accolades, including the Carrier President’s Award and the Angie’s List Super Service Award.
- Energy Efficiency: Our maintenance services help improve your furnace's energy efficiency, saving you money on energy bills.
- Reliable Support: We are always available to address your furnace concerns and provide prompt, reliable service.
Choose us for your furnace solutions in Austin, and experience the difference our dedication and expertise can make. Your comfort is our priority, and we are here to ensure your furnace operates at its best.
Call us today at (512) 379-6385 or contact us online for expert furnace solutions in Austin.
FAQs on Furnace Service in Austin
What Are Common Furnace Repairs in Austin?
Owing to Austin's specific climate, furnaces often encounter unique challenges that may necessitate repairs. Common issues include clogged filters due to dust accumulation, ignition problems because of humid conditions, and wear and tear from frequent use during colder months. Another prevalent issue is damage to the blower motor or belts, which can result from debris or insufficient lubrication. Regular maintenance checks can significantly reduce the likelihood of these problems, ensuring the furnace runs smoothly throughout its lifecycle.
How Often Should I Have My Furnace Serviced?
It's generally recommended to have your furnace serviced at least once per year, ideally before the onset of the cooler months. An annual service can help detect early signs of wear and prevent extensive damage. During service, technicians will clean and inspect parts, check for gas leaks, and ensure efficient operation. This preventive care not only prolongs your furnace’s life but enhances its efficiency, saving you money on energy bills.
Why Is My Furnace Making Unusual Noises?
Unusual noises in a furnace often indicate underlying issues such as loose components, a failing motor, or airflow problems. Rattling can be a sign of unsecured ductwork, knocking might point to issues in the burner, and squealing usually signals a worn belt. If you hear persistent strange noises, it's crucial to get a professional assessment to prevent further damage.
Are There Energy Efficiency Rebates Available in Austin?
Yes, several energy efficiency programs and rebates are available for Austin residents looking to upgrade or replace their furnaces. Check with local utility companies for incentives on Energy Star-rated appliances that meet efficiency standards. These rebates not only reduce the initial cost but also promote long-term savings on energy bills.
How Can I Improve My Furnace’s Efficiency?
Improving your furnace's efficiency involves several key practices. Begin with regular maintenance, including filter changes every 1-3 months. Seal leaky ductwork to prevent heat loss and ensure your home is adequately insulated. Installing a programmable thermostat can help control heating patterns and reduce wasted energy.
